+86-13516964051
+86-13516964051



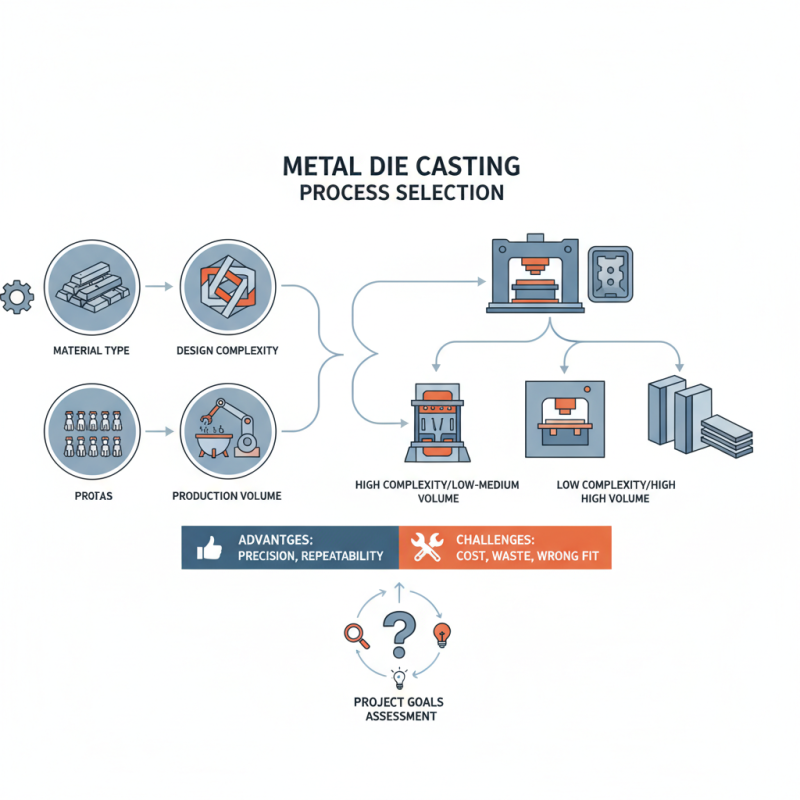
Choosing the right process for Metal Die Casting can significantly impact your project's outcomes. There are various methods available, each suited for different needs and applications. Factors such as material type, complexity of design, and production volume step into the spotlight.
Metal Die Casting leads to unique advantages like precision and repeatability. However, challenges can arise. Not every process fits every project, and making a wrong choice can result in increased costs or wasted materials. Consider those details closely.
Assessing your project's specific requirements is essential. Do you need high volumes or intricate designs? Understanding these factors is vital. Higher complexity may demand more advanced techniques, while simpler designs could benefit from basic methods. This choice can be difficult. Reflect on your project's goals to find the best fit.
Metal die casting is a crucial manufacturing process. It involves pouring molten metal into a mold. This mold shapes the metal into desired parts. Understanding the basic types of die casting is essential for project success.
There are primarily two methods: high-pressure die casting and low-pressure die casting. High-pressure casting is faster and produces high-quality parts. However, it may lead to more defects if not managed well. Low-pressure casting, in contrast, offers a more controlled process and is ideal for complex shapes. Yet, it generally takes longer. Choose based on your project's needs.
Tips: Consider the metal used. Aluminum and zinc are popular choices. Each metal has advantages and disadvantages. Think about the volume of production as well. High-volume needs fit high-pressure casting better. Low-volume projects might benefit from low-pressure methods.
Not all designs work well with any casting method. Some intricate designs may require more trial and error. Testing prototypes can help in refining your designs. There's always room for improvement and learning in this field. Keep iterating to achieve the best results.
| Process Type | Material | Typical Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Pressure Die Casting | Aluminum, Zinc | Automotive Parts, Consumer Electronics | High precision, Smooth surface finish | Higher initial tooling costs |
| Low-Pressure Die Casting | Aluminum, Magnesium | Large Automotive Components, Industrial Parts | Reduced porosity, Better mechanical properties | Slower production rates |
| Gravity Die Casting | Cast Iron, Aluminum | Heavy Machinery, Engineering Applications | Cost-effective for small runs | Lower precision than pressure die casting |
| Die Casting with Inserts | Aluminum, Magnesium, Zinc | Complex Parts with Reinforcements | Integrates multiple materials | Complex tooling and production process |
Choosing the right metal die casting process starts with understanding your project’s specific requirements. Consider the complexity of your design. Some products need intricate details, while others may focus on simplicity. This distinction can greatly influence which process suits you best.
Material selection is another critical factor. Different alloys offer unique properties. For instance, aluminum is lightweight, while zinc alloys provide corrosion resistance. Assess the end-use of your product. Will it face high temperatures or extreme conditions? Understanding the environment can guide your choice.
Production volume also plays a vital role. High-volume projects may benefit from a more automated process, such as high-pressure die casting. Conversely, small runs might lean towards lower-cost options. Balance between cost and quality can be tricky. Every project is unique and may require adjustments along the way. Evaluate your choices and embrace the learning curve of metal casting.
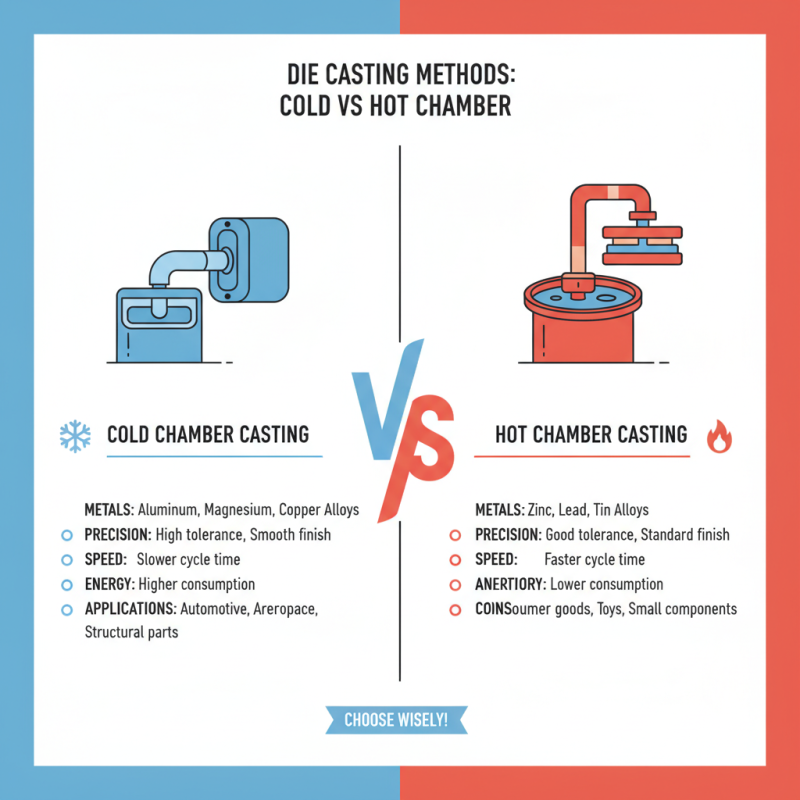
When it comes to selecting a die casting method, understanding the differences is crucial. There are several key processes to consider, such as cold chamber and hot chamber die casting. Cold chamber casting is ideal for metals like aluminum. It provides high precision and a smooth finish. However, it can be slower and requires more energy.
On the other hand, hot chamber die casting works best with low-melting-point alloys, such as zinc. This method is quicker and offers less waste. Yet, it may limit the types of materials you can use. Both methods have their pros and cons. Choosing the right one depends on your project's specific needs.
You should also think about the complexity of your design. Intricate shapes may pose challenges regardless of the selected method. Tooling costs can vary widely too. Sometimes, an apparently lower initial cost can lead to higher maintenance expenses later on. Weigh these factors carefully to avoid unexpected issues down the line.
When considering die casting for your project, material selection is crucial. Different metals have unique properties and costs. Aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant. It's ideal for automotive parts and consumer products. However, it can be more expensive than alternatives. Magnesium is another option. It's even lighter than aluminum but may not suit all applications.
Zinc offers excellent fluidity in casting, making it suitable for intricate designs. It's durable but might not have the same strength as aluminum. Copper, while costly, provides superior thermal and electrical conductivity. This can enhance performance in certain applications. Assessing your project's specific needs can guide you in choosing the right material.
Reflect on the project's intended use. What stresses will the part face? Consider the environment. Will it be exposed to high temperatures or corrosive conditions? Each material has strengths and weaknesses. Some choices will offer benefits but might come with trade-offs in cost or durability. Evaluating these factors allows for more informed decision-making in die casting projects.
When selecting a metal die casting process, assessing cost-effectiveness and production efficiency is crucial. Different processes have varying costs associated with setup, materials, and labor. For instance, high-pressure die casting offers quick turnaround times but might require a larger initial investment. Consider the specific demands of your project. Do you need intricate designs? Then investing in precision tooling may be worthwhile. But, if your design is simpler, a lower-cost option might suffice.
Production efficiency is equally important. High pressure die casting can yield thousands of parts quickly. However, was the initial investment justified? Reflect on potential waste too. Inefficient processes might lead to excess scrap or lower quality. Analyze the projected output against your budget. Sometimes, a balance between speed and quality can be tricky to strike. Ensure to carefully evaluate each method’s pros and cons in the context of your project’s goals and budget. What works for one application might not be ideal for another.