+86-13516964051
+86-13516964051



Zinc casting is an exciting technique for beginners. It offers endless possibilities for creativity and craftsmanship. As you dive into this world, you'll encounter challenges and learning moments.
This guide explores essential aspects of zinc casting. From selecting the right materials to mastering pouring techniques, every detail matters. You might face initial struggles, like achieving the perfect temperature or avoiding imperfections in your castings. Take your time to learn, practice, and refine your skills.
Zinc casting can transform raw materials into unique artworks. Enjoy the process and embrace the mistakes along the way. Remember, every expert was once a beginner. Let's embark on this journey together, learning and growing with each pour.
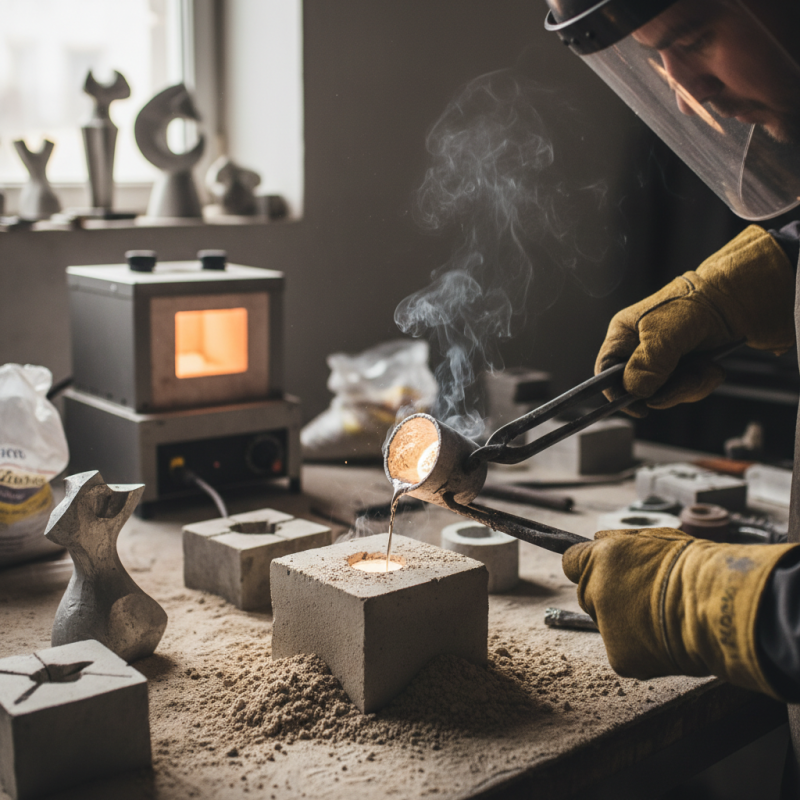

Zinc casting is a fascinating technique for creating metal parts. It involves pouring molten zinc into molds. This process is popular for its versatility and cost-effectiveness. Beginners often find zinc casting easier than other metals like aluminum. Understanding the basics is key to success.
When starting out, choosing the right mold is crucial. Silicone molds are a good option for beginners. They are flexible and easy to use. However, they might wear out quickly. Invest in high-quality molds for better longevity.
Tips: Always wear protective gear when working with molten metal. It is crucial to avoid burns or injuries. Practice patience. Your first pieces may not turn out perfect. Reflect on what went wrong. Adjust your technique next time to improve your results.
Zinc casting applications range from simple toys to complex machinery parts. The finished products often have a smooth finish. However, achieving that finish takes practice. Embrace imperfections as learning opportunities. These experiences will help refine your skills over time.
This chart illustrates the various zinc casting techniques and their applications based on percentage usage in different industries. The data highlights the importance of gravity casting, pressure die casting, and sand casting in the zinc casting domain.

Essential equipment is crucial for mastering zinc casting techniques. Beginners should focus on several key tools and materials. A melting furnace is at the top of the list. It allows you to reach the high temperatures needed to melt zinc, which has a melting point around 420°C. Proper temperature management can prevent defects in the final casting.
In addition, investing in a quality mold is vital. Different mold materials can affect the cooling rate and surface finish. Sand molds are popular due to their affordability and ease of use. However, they may result in rough surfaces. For more precise work, consider metal molds, though they come at a higher cost. Industry reports indicate that over 40% of beginners face challenges with mold durability. This suggests careful selection of mold types is essential.
Don’t overlook safety gear. Personal protective equipment including gloves, goggles, and aprons is a must. Zinc fumes can be hazardous, especially at elevated temperatures. Proper ventilation while melting zinc helps mitigate health risks. Many beginners underestimate equipment costs, which can lead to frustration as they progress. Choosing the right tools could enhance your learning curve and improve your casting outcomes significantly.
Zinc casting is an exciting process for beginners. To start, gather all necessary materials. You will need a furnace, zinc, molds, and safety equipment. Ensure your workspace is well-ventilated. Proper safety gear is essential. Otherwise, injuries can occur.
Begin by melting the zinc in the furnace. Monitor the temperature closely. This step requires patience. While waiting, check your molds for any defects. Ensure they are clean and dry. Pouring molten zinc into a flawed mold can lead to unfortunate results.
Once the zinc is melted, carefully pour it into the molds. Take your time. Rushing can cause spills or burns. After pouring, allow the zinc to cool completely. Finishing touches are vital. Sanding down sharp edges can make a significant difference in the final product. Mistakes are part of learning. Reflect on your first attempts and identify areas for improvement.
Zinc casting can be rewarding yet challenging. Beginners often face common obstacles. One frequent issue is the formation of air bubbles. These defects can compromise the surface finish and structural integrity. According to a report from the International Journal of Casting Technology, nearly 25% of casting failures stem from this problem. Adjusting the pouring rate is critical. Pouring too quickly invites air, while a slow pour might cause solidification before the mold is full.
Another challenge is controlling the temperature. Zinc has a relatively low melting point, typically around 420°C. However, overheating can lead to oxidation, resulting in poor quality. Notably, a study by the American Foundry Society indicates that maintaining optimal pouring temperatures can improve yield by up to 15%. Investing in proper monitoring tools can help you achieve this surprisingly crucial factor in casting success.
Beginners should also watch for contamination. Even dust on the surface can result in defects. Many novice casters overlook mold preparation. Ignoring this can waste resources and effort. Failures can be frustrating, prompting reflection and learning. Embracing these challenges as opportunities promotes growth in the craft. It's part of the journey toward mastering zinc casting techniques.
| Challenge | Description | Solution | Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porosity | Presence of tiny air pockets in the cast | Use proper venting and avoid rapid cooling | Ensure smooth pouring and maintain consistent temperatures |
| Inconsistent Surface Finish | Variations in texture and smoothness | Optimize mold design and sand casting techniques | Experiment with different sand mixtures and binders |
| Shrinkage | Reduction in volume during cooling | Incorporate appropriate risers in designs | Plan for additional material in critical areas |
| Metal Flow Issues | Improper flow leading to defects | Adjust gating systems for better metal flow | Review mold placement and temperatures |
| Cracking | Fractures occurring in the casting | Control cooling rates and temperatures | Avoid abrupt temperature changes during solidification |
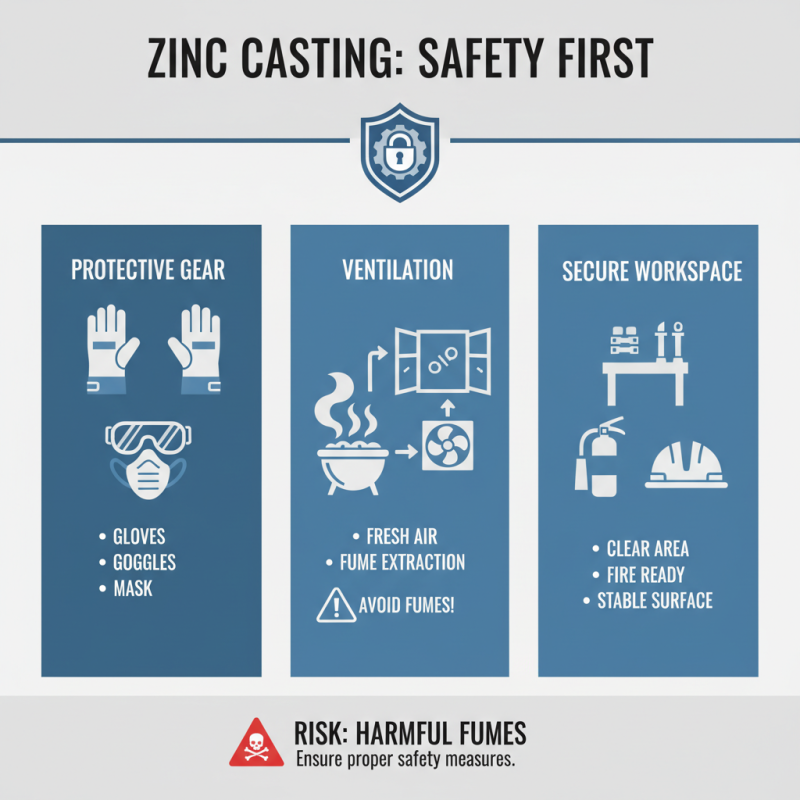
Zinc casting can be rewarding but involves risks. A secure working environment is crucial. Always wear proper safety gear, including gloves, goggles, and masks. Breathing in zinc fumes can be harmful. Ensure good ventilation in your workspace, especially when melting zinc.
Keep your area organized. Clutter can lead to accidents. Small spills may go unnoticed. They can create slippery surfaces, increasing the chance of slips. Use sturdy containers for molten zinc. If you notice any instability, reassess your setup. Safety must be prioritized at all times.
Regularly inspect your tools and equipment. Worn or damaged tools can be dangerous. Replace them immediately. Additionally, educate yourself about the materials you’ll be using. Understand their risks and proper handling procedures. Don't overlook these vital steps. Reflect on past mistakes to avoid future accidents. Mistakes in safety are often costly and can’t be taken lightly.