+86-13516964051
+86-13516964051



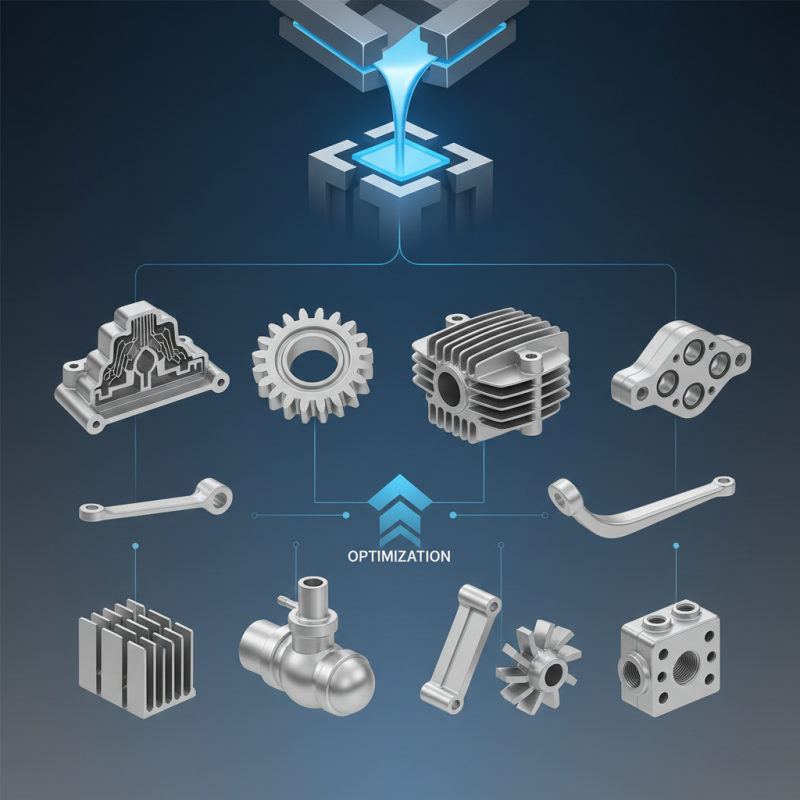
In the realm of manufacturing, die casting parts play a pivotal role in achieving precision and efficiency. As industries continue to evolve, understanding the various die casting parts becomes essential for optimizing production processes. This comprehensive guide delves into the top ten die casting parts that are crucial for manufacturers seeking to enhance their output and streamline operations.
Die casting is a process that allows for the creation of intricate shapes and designs with a high degree of detail, making it a preferred method for producing metal components. Each die casting part serves a specific function, contributing to the overall integrity and performance of the final product. From the design phase to assembly, recognizing the significance of each component and its impact on manufacturing can lead to substantial improvements in quality and cost-effectiveness.
As we explore these ten essential die casting parts, readers will gain insights into their applications, advantages, and best practices. Whether you are new to the field or an experienced professional, understanding these die casting parts will empower you to make informed decisions that enhance production efficiency and elevate your manufacturing capabilities.

Die casting is a highly efficient manufacturing process that involves forcing molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. This technique allows for producing complex shapes with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy, making it a preferred method for many industries. The process begins with the selection of the appropriate metal alloy, which significantly influences the final properties of the casting. Common materials used in die casting include aluminum, zinc, and magnesium due to their favorable mechanical properties and lightweight nature.
Tips for successful die casting: ensuring mold design is robust and incorporates features that facilitate easy ejection of the final part. Additionally, maintaining optimal temperature control of the molten metal is crucial, as it affects flow characteristics and solidification rates. It’s also essential to perform regular maintenance on the die casting machines to prevent wear and ensure consistent quality over time.
In order to achieve the best results, consideration should be given to the cooling system within the mold. Efficient heat management not only enhances the quality of the parts produced but also can reduce cycle times, thereby increasing overall productivity. By understanding these fundamental aspects of the die casting process, manufacturers can significantly improve their operational efficiency and product quality.
Die casting is a manufacturing process that utilizes high pressure to force liquid metal into a mold cavity. The choice of materials is crucial in determining the quality and performance of the final product. Traditionally, aluminum and zinc have been favored due to their desirable properties. Aluminum offers excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight, and good thermal conductivity, making it a prime choice for various applications, including automotive and aerospace components. Zinc, on the other hand, is known for its durability and ability to maintain dimensional accuracy, making it suitable for intricate designs and small, complex parts.
In addition to aluminum and zinc, magnesium has gained popularity in die casting due to its light weight and high strength-to-weight ratio. This metal is particularly advantageous in industries seeking to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions without compromising structural integrity. Furthermore, copper-based alloys are utilized for their excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, particularly in the production of components like electrical connectors and heat sinks. Understanding the properties of these materials is vital for manufacturers aiming to optimize the die casting process and ensure the production of high-quality, reliable parts.
Die casting is a manufacturing process that offers numerous benefits, particularly in the production of complex metal parts. One of the most significant features of die casting components is their ability to achieve tight tolerances and high dimensional accuracy. This precision is vital in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where even the smallest deviation can lead to performance issues or safety risks. The process utilizes molten metal, typically aluminum, zinc, or magnesium, which is injected into a mold under high pressure. This allows for the creation of intricate shapes and details that are often impossible with other manufacturing methods.
In addition to accuracy, die casting components provide excellent surface finishes, reducing the need for secondary operations like machining or polishing. The inherent strength and durability of die cast parts also contribute to their popularity; they can withstand harsh environments and heavy use without significant wear. Furthermore, die casting enables high-volume production, making it an efficient choice for manufacturers looking to maintain cost-effectiveness while meeting demand. The combination of these features—precision, aesthetic quality, strength, and efficiency—highlights why die casting is a preferred method for producing essential components in various industries.
| Part Name | Material | Typical Applications | Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transmission Housings | Aluminum | Automotive Transmissions | Lightweight, Durable | Improves fuel efficiency |
| Engine Blocks | Aluminum, Magnesium | Automotive Engines | Strength, Corrosion Resistance | Longer lifespan |
| Pump Bodies | Aluminum, Zinc | Hydraulic and Water Pumps | Precision, Tight Tolerances | Enhanced efficiency |
| Brackets and Clamps | Aluminum, Zinc | Construction, Automotive | Lightweight, Customizable | Versatile use |
| Motor Housings | Aluminum | Electric Motors | Heat Dissipation, Lightweight | Improved performance |
| Chassis Components | Aluminum | Automotive | Sturdy, Impact Resistant | Safety and durability |
| Electrical Enclosures | Aluminum, Zinc | Electrical Equipment | Protection, Heat Resistance | Safeguards components |
| Valve Bodies | Aluminum | Fluid Control Systems | Complex Geometry, Precision | Reliable operation |
| Clutch Cases | Aluminum | Automotive | Lightweight, Strong | Enhances performance |
| Frame Components | Zinc, Aluminum | Cameras, Robotics | Strength, Lightweight | Improves stability |
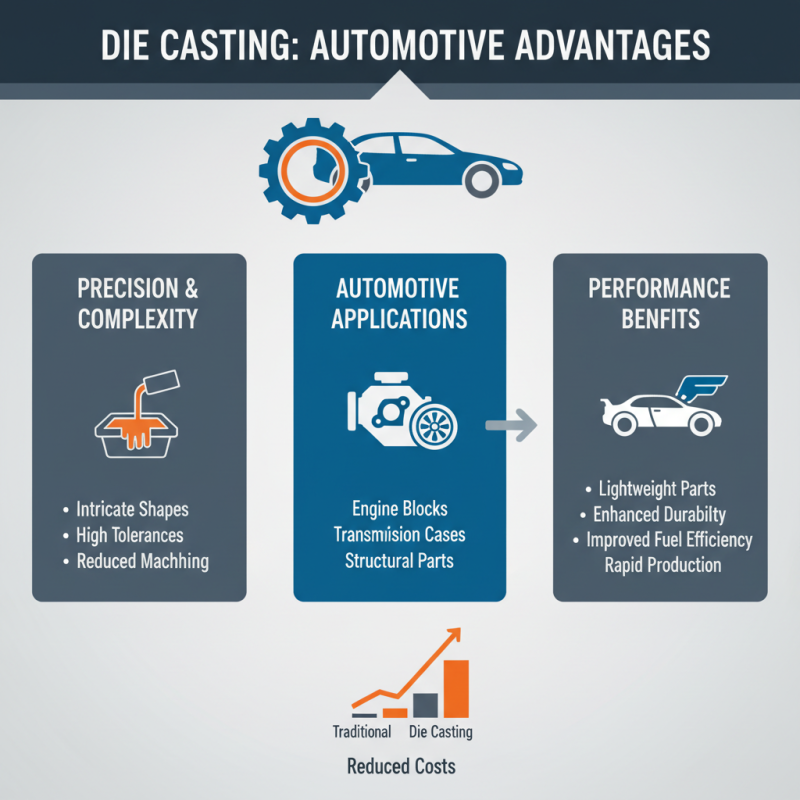
Die casting is a vital manufacturing process employed across various industries due to its efficiency and ability to create intricate shapes with high precision. One of the primary applications of die casting is in the automotive sector, where components such as engine blocks, transmission cases, and structural parts are produced. The durability and lightweight nature of die-cast parts contribute significantly to improving vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. Additionally, the automotive industry benefits from the rapid production rates offered by die casting, ensuring timely delivery and reduced costs.
Another prominent application of die casting can be found in the electronics industry. Components like housings for electronic devices, connectors, and heat sinks are commonly manufactured using this method. The fine details and excellent surface finishes achievable through die casting allow for the optimal performance of electronic products, enhancing their reliability and aesthetic appeal. Moreover, die casting enables the production of complex shapes that would be challenging or costly to create using other manufacturing techniques, making it a preferred choice for many electronic applications.
To optimize die casting manufacturing, it is crucial to focus on the preparation phase, as it sets the foundation for quality and efficiency. One of the best practices is to conduct a thorough design evaluation. By using computer-aided design (CAD) tools, manufacturers can identify potential issues early on, such as weak points in the structure or difficulties in part release. Additionally, ensuring that the mold design incorporates proper gating and venting will facilitate smoother molten metal flow and gas release, thereby minimizing defects during the casting process.
Another key aspect for optimization is closely monitoring the die casting process parameters. This includes maintaining consistent temperatures and pressures to achieve uniformity in the cast parts. Implementing advanced technology, such as sensors and data analytics, can help in real-time monitoring and control of these parameters. Furthermore, routine maintenance of the dies is essential to prevent wear and tear that can lead to inconsistencies. By adhering to these best practices, manufacturers can enhance productivity, reduce waste, and ultimately improve the quality of their die-cast components.